It is important that you keep your blood pressure under control to avoid complications of hypertension.
High blood pressure that remains uncontrolled over a long period of time can cause excessive pressure on artery walls. This pressure can damage blood vessels and even organs in the body. The complications of hypertension that can result from uncontrolled high blood pressure include the following.
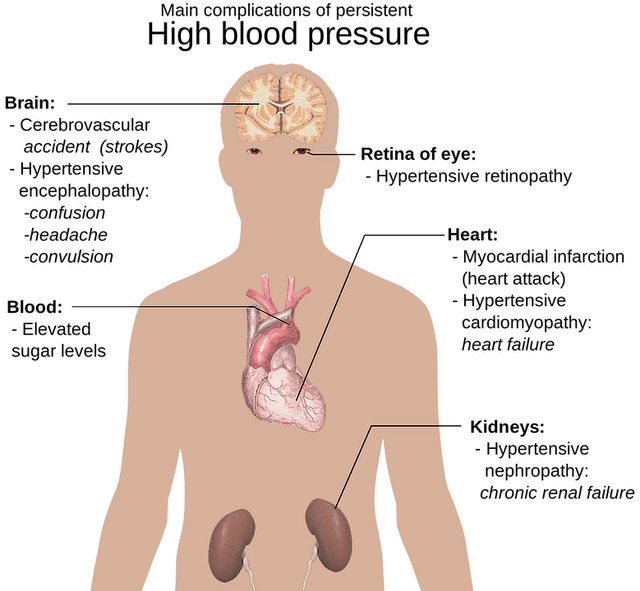
Stroke is one of the complications of hypertension
Stroke is a leading cause of death and severe, long-term disability. Hypertension is the leading cause of stroke and is said to cause more than half of them. If you have had a stroke, you are likely to also have had hypertension (high blood pressure). According to experts, strokes can be prevented. One very good way to reduce the risk of stroke is to maintain your blood pressure within a healthy range of 120/80 mmHg or below. When your blood pressure is always high, it means your heart is pumping harder than it should. Research shows that this is an important risk factor for having a stroke.
High blood pressure puts your arteries under constant stress which damages arteries around the body. Too much force in the arteries make them weaker and creates a condition where they can burst or clog more easily. Weakened arteries in the brain caused by high blood pressure, put you at a much higher risk for stroke
Strokes can be of two types and having high blood pressure puts you at risk of developing both types. The two types are ischemic stroke when blood vessel in the brain are blocked by a clot or haemorrhagic stroke when blood vessels in the brain bursts.
Ischemic Stokes
Most strokes are ischemic strokes and are caused by blocked blood flow to the brain. The blockage is usually caused by a clot. Hypertension causes clot to form more often than normal as it speeds up arteriosclerosis, which is a condition which makes the arteries narrower, harder and clogged with fatty plaque. Clots usually form in clogged blood vessels.
High blood pressure also increases your risk of developing atrial fibrillation which is when you have an irregular heartbeat. Atrial fibrillation causes blood to collect and form a pool where clots can easily form. This clot can then travel to the brain and cause a stroke. Atrial fibrillation increases your chances of getting strokes by to up to five folds.
When clots block the blood flow to the brain, that part of the brain is no longer getting the oxygen it needs, so it starts to die within minutes. Your brain controls your movement, thoughts and speech, so a stroke can affect your ability to think, move, speak or comprehend spoken words. It can also affect language, vision, memory and may even cause paralysis or death.
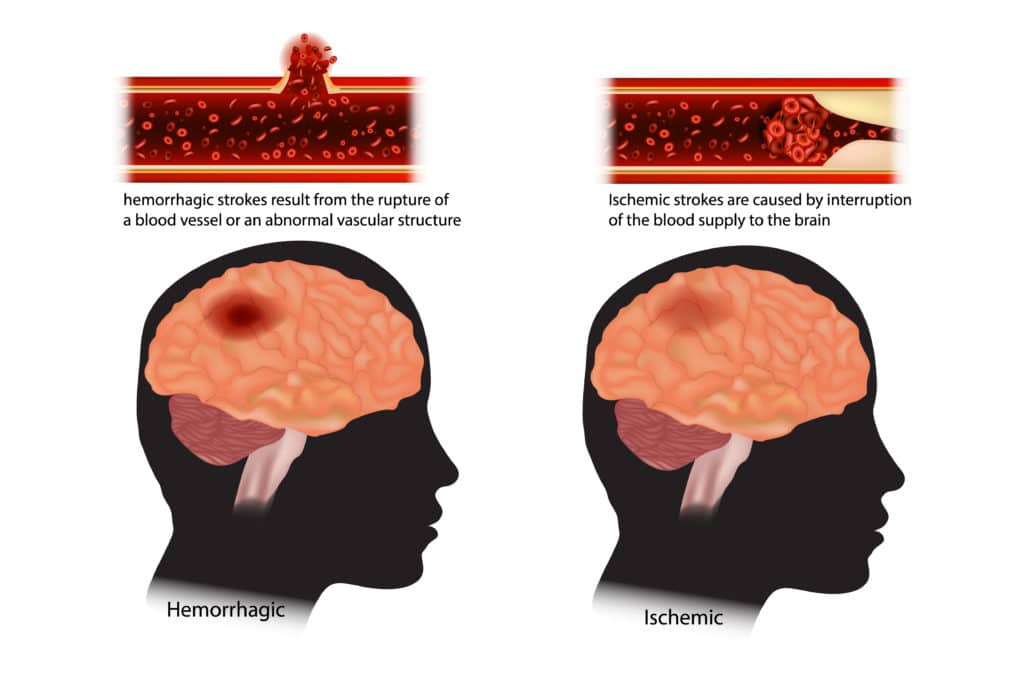
Haemorrhagic Stroke
This type of stroke is less common than ischemic stroke but tend to be more serious and more fatal. They are caused by bleeding from ruptured blood vessel either in or around the brain. Subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) refers to bleeding on the surface of the brain while Intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) is bleeding deep within the brain. Hypertension weakens and damages arteries and makes them more likely to tear or burst.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) or mini strokes
This is caused by a temporary clot. High blood pressure can cause clots that lead to temporary clot which dissolves or gets dislodged on its own. Most people will fully recover from TIAs, but they are a warning that a full-blown stroke may be eminent. Hypertension causes clot to form more often than normal as it speeds up arteriosclerosis, which is a condition which makes the arteries narrower, harder and clogged with fatty plaque. Clots usually forms in clogged blood vessels.
Heart attack – one of the complications of hypertension
High blood pressure puts your arteries (including your coronary arteries which supply blood to your heart muscles) under constant stress which damages arteries around the body. This constant stress causes the coronary arteries to slowly become narrowed from a build-up of fat, cholesterol and other substances which together are called plaque. This process is known as atherosclerosis.
A heart attack is when one of the coronary arteries becomes blocked due to an accumulation of plaque or a blood clot. This starves the heart muscle of vital oxygen and nutrients and, if not treated, will begin to die. The damage or death of part of the heart muscle is what is referred to as a heart attack or myocardial infarction.
Heart Failure – one of the complications of hypertension
Heart failure is when your body is unable to pump blood to the body as well as it should. When your blood pressure is high, the workload to your heart is increased. This happens because the force pushing on the walls of your arteries as blood moves through them is too strong. This strong pressure causes your arteries to tear and turn into scar tissue where cholesterol, fat, and other substances can build up and make your blood vessels to narrow and stiffen.
The narrowing and blocking of blood vessels increase your risk of developing heart failure. Arteries which are narrow and stiff making it harder for the blood to travel smoothly and easily throughout your body and causes your heart to work harder.
Over time, the increased workload leads to an enlarged heart. In order to cope with this extra effort, the heart thickens and becomes stiffer and larger. While it is still able to pump blood, it becomes less efficient. The larger the heart becomes, the harder it works to meet your body’s demands for oxygen and nutrients.
Vision Loss – one of the complications of hypertension
Your eyes have very many tiny blood vessels. When your blood pressure remains high over a long time without being treated, several conditions which affect your vision can develop.
Hypertensive retinopathy
High blood pressure can cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina which is the area at the back of the eye where images focus. This happens when there is lack of blood flow to the retina and can lead to blurred vision or even loss of eyesight. This is referred to as hypertensive retinopathy.
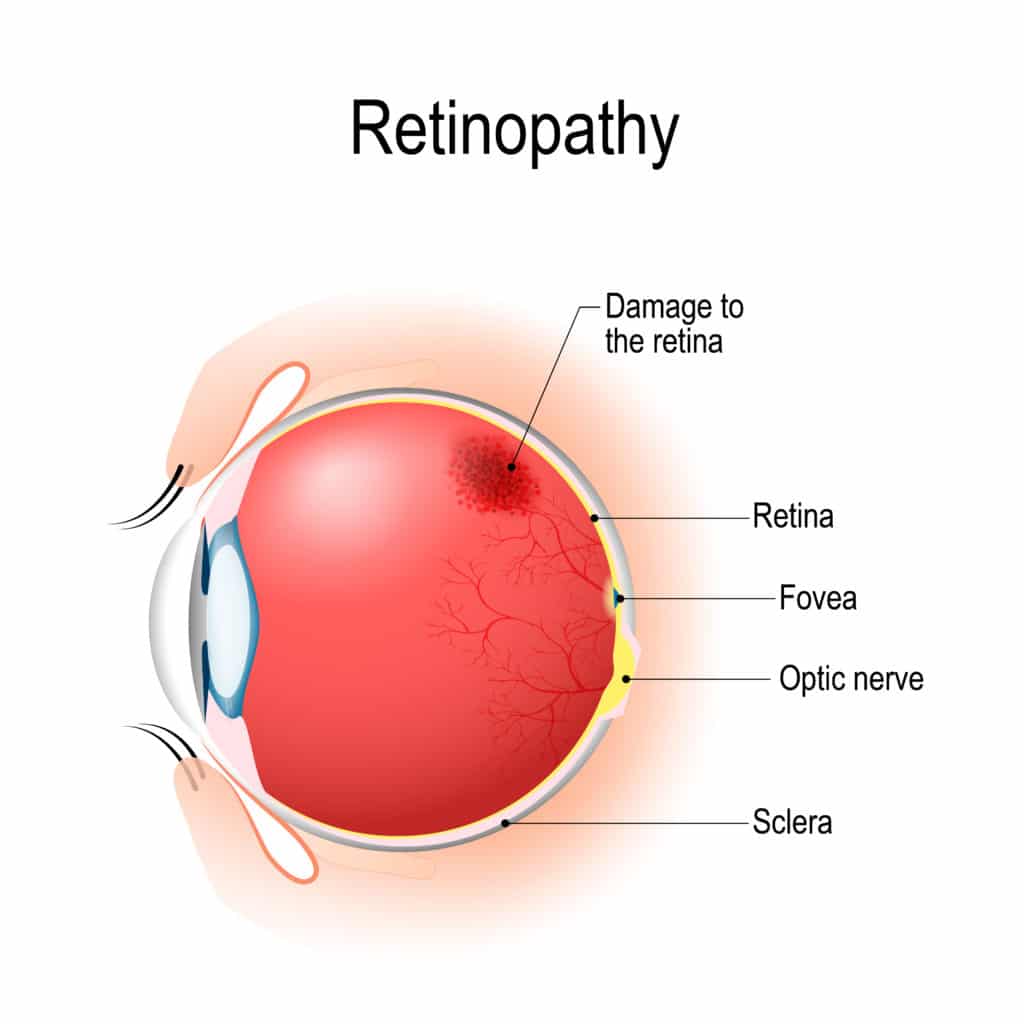
Choroidopathy
This is when fluid build-up under the retina and cause distorted vision or scarring that impairs vision.
Optic neuropathy
This happens when lack of blood flow kills the nerve cells and damages the optic nerve. This can cause temporary or permanent loss of vision.
Stroke which which is one of the complications of hypertension can impair the optic nerve or damage the part of the brain that processes images and cause vision loss.
Kidney damage is one of the major complications of hypertension
High blood pressure can cause kidney disease and kidney disease can cause high blood pressure. Kidney disease is when your kidneys are not working as well as they should. Your kidneys are a pair of regulatory organs found on either side of your back. Their main function is to filter your blood to remove unwanted waste products and excess fluid from the body. The nephrons are part of the kidney that filter your blood. These nephrons receive their blood supply through a dense network of blood vessels and a high volume of blood flows through them.
When blood pressure remains consistently high over a long period of time, the arteries around the kidneys become weakened, narrow and hardened. This damaged artery is unable to supply enough blood to the nephrons which means the nephrons do not receive the essential oxygen and nutrients causing the kidneys to lose the ability to perform its function which is to filter blood and regulate the fluid, hormones, acids and salts in the body. Kidneys also produce aldosterone which helps in regulating blood pressure. When your kidneys are damaged by consistently high blood pressure, your kidneys fail to give the right signal to produce this hormone which means blood pressure is not regulated.
You can read more about how high blood pressure can affect the kidneys here.
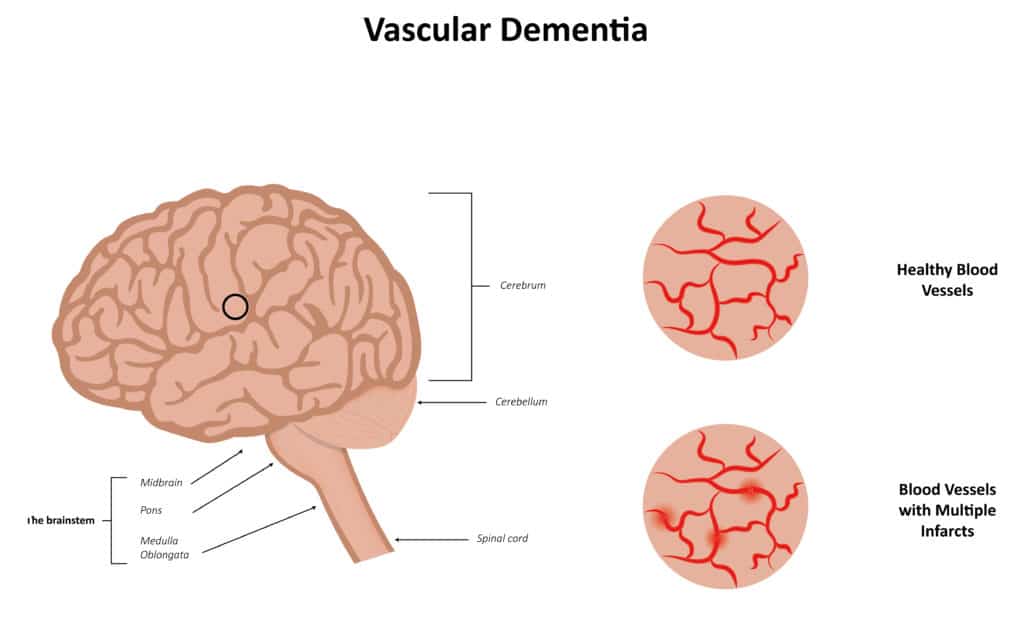
Vascular Dementia – one of the complications of hypertension
When blood pressure remains high for a long time without treatment, the blood vessels around the brain may become narrow, damaged and this may increase the risk of your blood vessels becoming blocked or bursting. When any part of the brain is starved of oxygen and nutrients because of a blocked or burst blood vessel, some cells in that part of the brain may be damaged, or even die. This damage can sometimes affect a person’s ability to speak and understand. Over time, there can be a recurrent blocking of different small blood vessels in the brain, this can also cause memory loss and confusion. This is what doctors refer to as vascular dementia.
Sexual dysfunction – one of the complications of hypertension
High blood pressure can cause damages to blood vessels and reduces blood flow throughout your body. Reduced blood flow to the pelvis can affect the sex lives of both men and women.
When blood pressure remains consistently high over a long period of time, the arteries around the penis may become weakened, narrow and hardened or even burst. This damage to the arteries can cause reduced blood flow to your penis. Erectile dysfunction occurs when there is not enough blood flow to the penis to allow for an erection.
High blood pressure may cause women to have lower libido and less interest in sex. A woman’s blood flow to her vagina may be reduced as a result of damaged arteries caused by persistent high blood pressure and may affect how her body responds to sex.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) – one of the complications of hypertension
When blood pressure remains high for a long time without treatment, the arteries around the periphery may become narrow. This narrowing is caused by the build-up of plaque which reduces blood flow. This plaque may then become inflamed and rupture, Triggering the formation of blood clots which can either make the arteries narrower or completely block it.
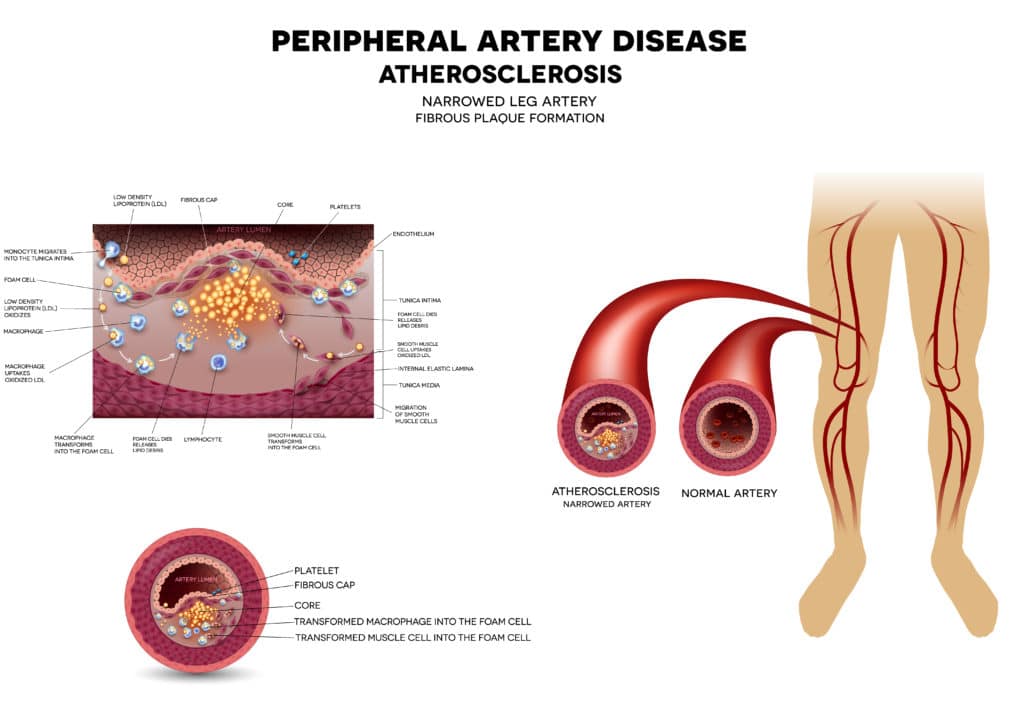
Peripheral in case of the heart means away from the heart. Peripheral artery disease is when the peripheral arteries supplying the arms, head, legs and stomach become narrow and cause painful cramps, difficulty walking, changes in skin colour, and sores or ulcers. The most commonly affected arteries are those supplying the legs. Total loss of blood supply to the legs and feet can cause gangrene and even loss of a limb.
About the author
Nwasom is a pharmacy graduate and a pharmacist currently practising in the United Kingdom. I have great experience communicating with patients and their family as gained through working as a pharmacist in both the hospital and community pharmacy sector. I love writing so it was a natural thing to try and pass medical and health information on through writing.
